Concrete Cylinder Calculator
Results:
Concrete Cylinder Volume Formula
Using measurements in feet:
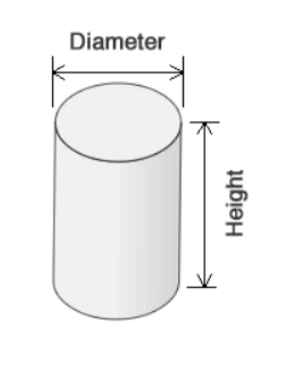
Area of the Circle (ft2):
\( \text{Area} = \pi \times \left( \frac{\text{Diameter}}{2} \right)^2 \)
Volume in Cubic Feet (ft3):
\( \text{Volume}_{ft^3} = \text{Height} \times \text{Area} \)
Volume in Cubic Yards (yd3):
\( \text{Volume}_{yd^3} = \frac{\text{Volume}_{ft^3}}{27} \)
Volume in Cubic Meters (m3):
\( \text{Volume}_{m^3} = \text{Volume}_{ft^3} \times 0.0283 \)
Value of Pi (\( \pi \)): \( 3.14 \)
Design Notes for Pouring Concrete Cylinders
Pre-pouring Preparations
- Ground Bearing Capacity: Ensure the ground where the cylinders will be poured has sufficient bearing capacity to prevent sinking or tilting.
- Formwork Inspection: Verify the formwork dimensions against the required cylinder dimensions and ensure material specifications meet design requirements.
- Formwork Preparation: Apply release agent evenly to the formwork to facilitate removal after pouring.
- Reinforcement Acceptance and Fixation: Inspect reinforcement for quality and fix reinforcement cages to ensure accurate positioning and stability.
Pouring Process
- Base Preparation: Wet the base before pouring and fill with 5-10 cm of 1:2 cement mortar to enhance density and prevent honeycombing.
- Layered Pouring: Pour concrete in layers not exceeding 50 cm in thickness, especially for taller cylinders.
- Vibration Technique: Use an immersion vibrator to vibrate the concrete evenly and fully, avoiding touching the reinforcement.
- Free Fall Height: Ensure the free fall height of concrete from the chute does not exceed 2 meters; use a chute extension if necessary.
- Pouring Height: For vertical structures exceeding 3 meters in height, use a chute, tremie, chute with side openings, or other suitable method.
Post-pouring Care
- Watering and Curing: Start watering the concrete surface after initial setting (usually 2-4 hours), maintaining it wet for at least 7 days, depending on climate and concrete type.
- Environmental Adaptation Strategies: Adjust watering frequency and methods based on temperature, wind speed, and other environmental conditions.
Additional Considerations
- Safety Precautions: Ensure the safety of personnel during pouring operations by wearing necessary protective equipment.
- Quality Control: Strictly control the quality of concrete, including mix proportions, pouring uniformity, and vibration.
- Construction Records: Keep detailed records of pouring data, such as pouring time, height, and vibration frequency, for quality control and troubleshooting.
 Home
Home Back
Back